-
Lower Extremity Joint Stiffness During Running in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder
2022Lauren A. Luginsland MS, Justin A. Haegele PhD, and Hunter J. Bennett PhD
During late adolescence, children undergo rapid skeletal growth changes leaving the child more vulnerable to injury during physical activity. This is consistent for autistic youth, who reportedly enjoy individual activities, such as running, more than team-based sports [1-3]. Inadequate joint stiffness is one of several factors that may influence injury risk [4]. The purpose of this study was to examine lower extremity joint stiffness in autistic and non-autistic matched controls at self-selected and matched running speeds.
Twenty-two persons with a confirmed autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis and seventeen age, sex, and body mass index controls (CON) were enrolled into the study. Position and force data were collected in the Neuromechanics Laboratory using the motion capture system. Participants were asked to complete a series of over-ground running trials at their self-selected speed and a standardized speed of 3.0 m/s.
Joint stiffness was calculated as the quotient of the change in joint moment and the change in joint angle during the energy absorption period of stance. Statistical analyses were performed in SPSS (version 27, IBM Corp.). Stiffness and changes in joint moments were analyzed using 2 (group) x 2 (speed) analyses of variance.
There were no significant interactions between groups and speeds (p>0.05) for any variable. Persons with ASD had reduced knee and ankle joint stiffness (all p
Persons with ASD had reduced lower extremity stiffness, which was due to their reduced joint moments. Decreased joint stiffness by those with ASD could be indicative of a less efficient running style whereby the elastic recoil is not being optimally utilized.
-

Study of Glucose Supplementation on Antibiotic Efficacy Against Staphylococcus aureus
2022Areej Malik, Alexandra E. Chittams-Miles, Claudia Muratori, and Erin B. Purcell
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), is a Gram-positive, facultative anaerobic, biofilm-forming bacterium. It is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) in the United States. The public health impact of S. aureus has been increased by the emergence of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It has also shown intermediate resistance to Vancomycin, which suggests that full resistance may develop. It is known that hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) from diabetes reduces immune system function. Patients with diabetes experience a greater rate of skin and soft tissue infections. This research explores the effect of increasing glucose concentration on S. aureus response to multiple classes of antibiotics to determine whether hyperglycemia could contribute to treatment failure of diabetic S. aureus SSTIs. Our results support the claim that hyperglycemia will not contribute to treatment failure of diabetic SSTIs while working with different classes of antibiotics.
-

An Importance-Performance Analysis of Local and Destination Visitors to Monocacy National Battlefield
2022Colin McCormack, McKenzie Mosher, Caleb Scruggs, Chris Zajchowski, and Jessica Fefer
The purpose of this study was to understand the evolving visitor experience at Monocacy National Battlefield (MONO) in Fredrick, Maryland and, specifically, the way this National Park Service site serves both its’ tourist and local visitors. MONO has two main demographics who utilize it: individuals seeking to learn about historical importance of the site in the Civil War and local recreational visitors from Frederick and surrounding communities. Due to MONO’s proximity to the more densely populated area of Fredrick and Civil War roots, it appeals to both of these populations, who find different uses in the park. Accordingly, we were asked to assist the Park, in better understanding the similarities or differences between visitors desired amenities, opportunities, and experiences at the Park to guide future investment, planning and management. To gauge visitors’ perceived importance and performance across different characteristics, an Importance-Performance questionnaire was developed. This process “provides businesses and organizations with a fairly clear assessment of where they are performing well and where improvements are required” (Draper, 2016; Martilla & James, 1977). Following survey design and approval, onsite sampling occurred over 21 visitor contact days in summer and fall of 2021. 469 visitors were contacted across five sites of interest identified by the park. 445 visitors agreed to participate, yielding an acceptance rate of 94.9 percent. Surveys were conducted online and completed by visitors following their visit. 287 visitors completed more than half of the survey yielding a 61.2 percent response rate. Emerging results suggest key differences and similarities across visitor types.
References
Draper, J. (2016). Applying importance-performance analysis to services of a visitor information center. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 18(1), 84–95. doi: 10.1177/1467358415627300
Martilla, J., & James, J. (1977). Importance-Performance Analysis. Journal of Marketing, 41(1), 77-79. doi:10.2307/1250495
-

Lattice Optics Optimization for Recirculatory Energy Recovery Linacs with Multi-Objective Optimization
2022Isurumali Neththikumara, Todd Satogata, Alex Bogacz, Ryan Bodenstein, and Arthur Vandenhoeke
Beamline optics design for recirculatory linear accelerators requires special attention to suppress beam instabilities arising due to collective effects. The impact of these collective effects becomes more pronounced with the addition of energy recovery (ER) capability. Jefferson Lab’s multi-pass, multi-GeV ER proposal for the CEBAF accelerator, ER@CEBAF, is a 10- pass ER demonstration with low beam current. Tighter control of the beam parameters at lower energies is necessary to avoid beam break-up (BBU) instabilities, even with a small beam current. Optics optimizations require balancing both beta excursions at high-energy passes and overfocusing at low-energy passes. Here, we discuss an optics optimization process for recirculatory energy-recovery linacs (ERLs) using multi-objective evolutionary search methods.
-

Hacking the Mind: Internet Memes as Tools of Propaganda
2022Joshua Nieubuurt
Internet memes are one of the latest evolutions of “leaflet” propaganda and an effective tool in the arsenal of digital persuasion. In the past such items were dropped from planes, now they find their way into social media across multiple platforms and their territory lacks spacial boundaries. Internet memes can be used to target specific groups to help build and solidify tribal bonds. Due to the ease of creation, and their ability to constantly reaffirm axiomatic tribal ideas, they have become an adroit tool allowing for mass influence across international borders. This poster seeks to display some of the common links between internet memes and leaflet propaganda. This poster particularly focuses on the tools used to “hack” the attention of anyone connected to internet using dense modality, cognitive biases, and traditional PSYOP tactics that are rooted in earlier leaflet propaganda techniques. It is a brief snapshot of some of the more potent facets of a project published in 2021 (Internet Memes: Leaflet Propaganda of the Digital Age). The original text can be found here: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcomm.2020.547065/full
-

Clostridioides difficile Spore Production in Response to Antibiotic and Immune Stress
2022Adenrele Oludiran and Erin B. Purcell
Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile, an anaerobic, spore-forming Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium, is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections and can persist as surface-attached biofilms for protection from antibiotic and immune stress. C. difficile can form biofilms as a single species or with other anaerobic intestinal bacteria. The environmental signals that cause individual cells to secrete toxins, form biofilms, or develop into spores that can spread the infection to new patients are unknown. In these studies, we investigate bacterial responses to different stress. Antimicrobial host-defense peptides (HDPs) produced by animal immune systems are promising candidates to develop novel therapies for bacterial infection because they cause oxidative stress that damages multiple targets in bacterial cells, so it is difficult for bacteria to evolve resistance to these attacks. We investigate antibiotic treatments, metal ions and sugars, and antimicrobial peptide treatments to determine how. C. difficile reacts to multiple environmental stresses like those from antibiotic treatment or the human immune system. In our investigation of C. difficile and HDPs in an anaerobic environment, we found that the interaction of piscidin and copper is different in different oxygen environments. Antibiotics and oxidative stresses from other sources cause the cells to form spores and/or biofilms to protect themselves, but piscidin kill vegetative C. difficile cells without triggering these protective responses. Piscidins are highly active against C. difficile and could be a good candidate for drug development.
-
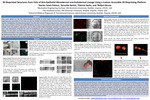
3D Bioprinted Structures from Cells of Non-Epithelial Mesodermal and Endodermal Lineage Using a Custom Accessible 3D Bioprinting Platform
2022Xavier-Lewis Palmer, Annette Berkin, Patrick C. Sachs, and Robert D. Bruno
Prior work within our lab has demonstrated the ability to print both murine and human mammary organoids and tumoroids in vitro that can also be reliably transplanted into a murine host for translational studies. Peripherally, this bioprinting system has also been used for 3D printing neurons, stem cells, cancer cells, and a primary cell line rich with fibroblasts, but each of these efforts were with cells of ectodermal lineage. Thus, the system's capacity for use on cells of other origins had been untested. To address this, we have now developed protocols for cells of endodermal and non-epithelial mesodermal/mesenchymal lineage. In this work, we find that we can produce reliable organoids, tumoroids, and other in vitro structures from them, thus expanding the functional range of our open 3D bioprinting platform. Therefore, we demonstrate that our system is versatile for adaptation to multiple cellular systems and can be applied to the work of labs that wish to study development and pathologies in other organ systems
-
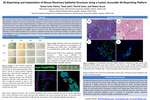
3D Bioprinting and Implantation of Mouse Mammary Epithelial Structures Using a Custom Accessible 3D Bioprinting Platform
2022Xavier-Lewis Palmer, Saad Jafri, Patrick C. Sachs, and Robert D. Bruno
Prior work has shown that our bioprinting system can reliably produce human mammary organoids and tumoroids with high precision. However, this was not previously applied to mouse models, which are also important with respect to translational research in cancer drug development. To address this, we have produced protocols for the development of in vitro structures from murine mammary epithelial and tumor cells. Additionally, we assessed the translatability of both human and murine bioprinted organoids into mouse mammary fat pads over a period of 6 weeks. Our lab found that our produced organoids are reliable, they can survive in vivo, and meaningfully integrate within host systems. Therefore, we have demonstrated that our system is adaptable to both human and murine models, as it offers a unique methodology for in vivo transplantation of human or murine organoids into mice, which can boost research efforts in cancer therapy research.
-

Violence Against Healthcare Workers: an Epidemic within a Pandemic
2022Michaela Ramandanes
Violence and harassment towards healthcare workers has been an underlying problem throughout history. However, with the rapid and evolving onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the risks that healthcare workers face has been a focal topic of discussion among administration, staff and the public. What was once considered an occupational hazard is now being raised as a public health issue- an epidemic within a pandemic. This literature review seeks to identify the prevalence and causes of violence and harassment towards healthcare workers. Was healthcare violence as prevalent before COVID-19? Has violence increased because patient volume increased? Additionally, this review will determine the mental, physical and social effects on healthcare workers who have endured workplace violence. Current intervention methods will be evaluated and suggestions will be made to address this emergent public health issue.
-

A Pathway to Solving the Structure of cl-Par-4 Tumor Suppressor Protein: Challenges & Findings
2022Krishna Raut, Samjhana Pandey, Andrea M. Clark, Komala Ponniah, and Steven M. Pascal
Prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4) is a pro-apoptotic tumor suppressor protein. Down-regulation of this protein has been reported in a myriad of cancers. Conversely, up-regulation of Par-4 is found to be associated with several neurodegenerative disorders. Par-4 is unique in the sense it can selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells. For this, caspase-dependent intracellular cleavage of Par-4 is essential to produce the functionally active fragment, cl-Par-4 (caspase-cleaved Par-4). The cl-Par-4 protein inhibits the NF-κB-mediated cell survival pathway and causes selective apoptosis in various tumor cells.
Our laboratory is interested in determining the structure of cl-Par-4 and understanding it’s interaction with various proteins. Currently, we are using biophysical techniques such as circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and SDS-PAGE to characterize the structure of cl-Par-4 in the presence of various concentrations of monovalent and divalent ions, in order to shed light on the possible ion-specific role of cl-Par-4 in inducing structure and self-association of this protein. Results show that effects on cl-Par-4 conformation are ion-specific, and effects of divalent cations are considerably more pronounced than effects from monovalent cations. We have also found that the cl-Par-4 shows a better stability in presence of Cl- ions than in presence of SO42- ions. Further, with the help of D313K mutant of cl-Par-4, we investigated that charge-charge repulsion between similar charged amino acid residues in leucine zipper is responsible for high salt at neutral pH or low salt at low pH requirement of cl-Par-4. All these findings will be helpful in getting the structured conformation of cl-Par-4 and, therefore, determining the structure of this protein via X-ray crystallography or via nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
-

Exercise Interventions for Relieving Anxiety Symptoms for People with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review
2022Kathryn Riis
Background: Clinical anxiety is a common comorbidity in people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The focus of interventional therapies tends to be activities which improve gross motor function, communication, social interactions, and other behavioral skills. Certain forms of exercise have been successful in lowering anxiety levels while improving physical function.
Objective: The purpose of this systematic review was to examine the effectiveness of the use of exercise as an intervention to reduce anxiety in people with ASD.
Methods: Two databases, PubMed and Medline, were searched utilizing key terms. This yielded 35 articles for review. PRISMA systematic search procedures identified 9 studies meeting predetermined inclusion criteria. Participant characteristics, whether participants engaged in physical activity, anxiety-related outcomes, and research methodology was evaluated for each study. Each paper included was appraised and scored using Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions risk of bias tool.
Results: Evidence from 9 studies suggests that exercise can have benefits for people with ASD, including improvements in emotional response as scored by the Gilliam Autism Rating Scale, third edition (GARS-3) and the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), and a decrease the DSM-oriented anxiety scores after an exercise intervention. There was evidence of improved mood, sleep quality, social interactions, communication, and the presence of maladaptive behaviors across studies suggesting a global effect of anxiety on people with ASD.
Conclusion: The studies included in this systematic review provide moderate evidence that exercise can help improve emotional state and decrease levels of anxiety for people with ASD. However, more research must be done to fully understand the effects exercise can have on anxiety for people with ASD.
-

Active Polar Liquid Crystal Channel Flows: Analyzing the Roles of Nematic Strength and Activation Parameter
2022Lacey Schenk and Ruhai Zhou
Suspensions of active polar liquid crystalline polymers (APLC) exhibit complex phenomena such as spontaneous flows, pattern formations and defects. Using the Kinetic Model, which couples the Smoluchowski Equation and the Navier-Stokes Equations, we conduct numerical simulations of APLC in a microfluidic channel to investigate the competitive effect among different material constants, such as the nematic concentration (the strength of the potential for nematic order) and active strength (the individual nano-rods strength of their individual movement) with and without a pressure gradient. Both Dirichlet and Neumann boundary conditions on the mathematical model are employed. Steady states, including isotropic and nematic states, as well as periodic states are observed. Spontaneous flows reveal interesting geometries in polarity vector orientation and nematic director orientation, such as flow reversals and banded structures with multiple regions within the channel boundaries.
-

The Intersection Between Climate Change and Human Inequality: A Narrative Review
2022Julia Serwaa
Introduction: Although developed countries are the largest contributors to climate change, its impacts continue to adversely affect low-income countries at a disproportionate rate. The purpose of this analysis is to address the environmental and health impacts of climate change in low-income countries as opposed to developed countries.
Methods:
A narrative literature review was conducted using a web-based search from scientific databases. The databases utilized were: United National Library of Medicine, JSTOR, and SpringerLink. The reviewer assessed the following inclusion criteria: peer-reviewed publications from 2012 – 2022, the availability of the publication in English, and the categorization as original research, reviews, meta-analyses or systematic reviews.The following search terms were used: “climate change, climate justice, health disparities, agriculture, and low income.”
Results: This review found that climate change contributes immensely to the prevalence of infectious diseases, malnutrition, and morbidity and mortality. Additionally, these countries also face environmental calamities such as weather variability, droughts, and floods which are impacting agriculture.
Discussion: Though the effects of climate change can be seen worldwide, it’s vital to address its impact on vulnerable countries which do not have adequate resources to combat the health and agricultural repercussions. To ease the burden of climate change in low-income countries, policies addressing climate, energy, and health should be adopted globally.
-

A Machine Learning Approach to Denoising Particle Detector Observations in Nuclear Physics
2022Polykarpos Thomadakis, Angelos Angelopoulos, Gagik Gavalian, and Nikos Chrisochoides
With the evolution in detector technologies and electronic components used in the Nuclear Physics field, experimental setups become larger and more complex. Faster electronics enable particle accelerator experiments to run with higher beam intensity, providing more interactions per time and more particles per interaction. However, the increased beam intensities present a challenge to particle detectors because of the higher amount of noise and uncorrelated signals. Higher noise levels lead to a more challenging particle reconstruction process by increasing the number of combinatorics to analyze and background signals to eliminate. On the other hand, increasing the beam intensity can provide physics outcomes faster if combined with a highly efficient track reconstruction process. Thus, a method that provides efficient tracking under high luminosity conditions can significantly reduce the amount of time required to conduct physics experiments.
In this poster, we present a machine learning (ML) approach for denoising data from particle tracking detectors to improve the track reconstruction efficiency of the CLAS12 detector at Jefferson Lab (JLab). A noise-reducing Convolutional Autoencoder was used to process data for standard experimental running conditions and showed significant improvements in track reconstruction efficiency (>15%). The studies were extended to synthetically generated data emulating much higher beam intensity and showed that the ML approach outperforms conventional algorithms, providing a significant increase in track reconstruction efficiency of up to 80%. This tremendous increase in reconstruction efficiency allows experiments to run at almost three times higher luminosity, leading to significant savings in time (about three times shorter) and money. The software developed by this work is now part of the CLASS12 workflow, assisting scientists of JLab and collaborating institutions.
-

Designing a Program to Increase Enrollment and Retention of Hispanic Children in Public Health Insurance Programs in Virginia: Lessons Learned
2022Cara Tonn
Children who have ongoing healthcare coverage benefit from improved health, education, and economic outcomes due to increased preventive services use and regular school attendance. These factors play a crucial part in determining a child’s level of education and future economic status. However, children eligible for publicly funded health insurance remain uninsured or experience “churning” throughout childhood and adolescence. Barriers to healthcare retention include lack of program awareness and understanding of the application process and belief that healthcare coverage only provides marginal benefits. Additionally, denial due to incorrect paperwork also contributes to low retention rates. Children who live in non-English speaking households, belong to an ethnic minority group or are foreign-born are at an increased risk of being uninsured or retaining health insurance. However, Hispanic children have the highest rates among ethnic minority groups of those at an increased risk for remaining uninsured. Based on information from current research, technical reports, and informal interviews at the local level, the researcher identified the underlying causes for low enrollment and retention among children living in Chesapeake, Virginia. Through the Socio-Ecological Model lens, the researcher recommends interventions at the individual, interpersonal, and community levels for program development to increase enrollment and retention of Hispanic children in publicly funded health insurance programs in Chesapeake. Additionally, the program utilizes an interdisciplinary team and key community stakeholders to implement this multifaceted outreach program with interventions to increase awareness, provide information, facilitate, and aid in the application process. Finally, the researcher discusses lessons learned and considerations for future implementation.
-

Returning to a New Normal: A Study Examining Student's Perceptions and Experiences of Campus Reopening during COVID-19
2022Cara Tonn, Anne Dumadag, Hira Nadeem, Brenda Berumen-Flucker, Priyanka Patel, and Hadiza Galadima
Background: Existing research on the mental health and academic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic reports adverse effects during the early stages of the pandemic due to the abrupt campus closures. However, with the relaxation of some restrictions, college students are allowed to return to in-person learning amid new policies. This study aims to assess students' perceptions on several topics related to the pandemic during campus reopening.
Methods: A 22-question cross-sectional survey based on stratified sampling was conducted among 1,025 students at Old Dominion University, and responses were collected via QualtricsTM in January 2022. The survey records socio-demographic information, self-reported mental health services (MHS) use, and data on students' perceptions associated with campus reopening. Descriptive statistics were generated, and a multivariable penalized logistic regression was used to identify factors associated with MHS use during campus reopening.
Results: A total of 236 students completed the survey. More than half are female, non-Hispanic, White, and 18-24 years old. About 56.54% (n=134) of the respondents have not experienced online classes before the pandemic. Nearly 40.26% (n=93) students feel they have learned the same in an online course as in a traditional course since the pandemic. There is a greater increase in MHS use during the pandemic than pre-pandemic (19.57% vs. 13.92%). Only previous use of MHS was found to be statistically associated with MHS use during campus reopening (OR=7.33, 95%CI=(2.54, 21.17)).
Conclusion: The study revealed increased use of MHS during the pandemic among college students. Also, the respondents had generally positive views of online courses since the pandemic. Given these findings, study authors suggest increased consideration of students' mental health status as a facilitator of learning and a need for further evaluation of in-person versus online learning to restructure higher education courses to best meet the needs of students.
-

Allied Dental Students' DVI Learning Outcomes Following a Multimedia Module
2022Samantha Vest, Brenda Bradshaw, Marsha Voelker, Ann Bruhn, Tara L. Newcomb, and Sinjini Sikdar
This pilot project assessed cognitive and affective learning outcomes of allied dental students following a disaster victim identification (DVI) multi-media learning module.
A convenience sample (n=41) of senior dental hygiene and dental assisting students from two institutions completed an IRB-exempt descriptive pretest/posttest study to assess cognitive and affective changes resulting from exposure to a multimedia DVI learning module of a PowerPoint presentation with audio/video recordings. After completing the learning module, participants were presented with 10 sets of mismatched antemortem (AM) and postmortem (PM) digital bitewing radiographs to test their cognitive ability to indicate identification matches. The pretest/posttest survey was a researcher-designed seven item, 3-point Likert scale survey completed in Qualtrics by all participants to assess perceived learning outcomes.
Following the learning module, dental hygiene (n=27) and dental assisting (n=14) students accurately matched at least four out of five radiographic DVI sets for an accuracy rate of 80%. However, a Fisher’s exact test revealed a statistically significant (p=0.01269) increase of DVI match performance for dental hygiene students compared to dental assisting students. Most participants (n=38, 92%) indicated they felt moderately or extremely confident to assist with DVIs because of curricula from their respective programs. A linear trend test revealed a statistically significant (p< 0.05) increase in perceived cognitive knowledge of DVI dental radiology and morphology application skills for mass fatality incidents, and a statistically significant increase (p< 0.05) in perceived affective attitudes at the valuing level regarding perceived importance of their respective professions as DVI volunteers.
Results show a multimedia learning module may significantly increase allied dental students’ cognitive and affective abilities to aid in DVI efforts. Additional research with larger samples of allied dental students could provide more information about the efficacy of including such learning modules in curricula where there are current gaps.
-

The Impact of Oral Health on Low-Income Pregnant Women living in the United States
2022Olivia Ward and Jill Jacobs Diss
Introduction: Oral health has a significant impact on pregnancy outcomes. Inter-professional collaboration can assist in bridging the gap between oral and systemic health and assist in optimizing the health of low-income pregnant women, infants, and children.
Methods: A literature review was used to ascertain the impact of oral health on adverse pregnancy outcomes. Research sources used in this literature review were gathered from the U.S. National Library of Medicine at the National Institutes of Health, PubMed, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Elsevier, Department of Medical Assistance Services (DMAS), the Office of the Surgeon General, and Google Scholars. Inclusion criteria were pregnant women.
Results: Poor dental health during pregnancy can contribute to adverse pregnancy outcomes and contributes to early childhood caries. Conversely, many systemic diseases can present oral signs and symptoms. Low-income women are disproportionately affected due to limited or no access to oral health care through their health insurance, or due to poor quality health care. The socio-ecological model was used to identify factors that affect oral health at the individual, interpersonal, organizational, and public policy levels.
Discussion: Studies have shown that inter-professional collaboration with health care professionals and other non-dental professionals can improve pregnant women’s oral health. Prenatal care that includes oral health screening, education, and referrals can mitigate the risk of oral diseases during pregnancy and the postpartum period. A systems change approach can be utilized to create a collaborative effort in addressing this public health issue.
-

Site Selection for Norfolk Day Services Facility
2022Faith N. Witkowski and Hua Liu
In October 2021, The Center: A Temporary Shelter transitioned from its downtown location to a residential area a few blocks away. After the move, a pressing, geographic-based question has surfaced: what makes the best location for the houseless population to be able to utilize resources? Using two methods, this study endeavored to answer this question in multiple ways, through different lenses. Method one's objectives are to find an optimal location(s) for a potential Norfolk day service facility based on 1) proximity to social and health services, 2) proximity to a neighborhood that would most benefit from a day center, and 3) is easily walkable. Whereas the objectives of method two are to: 1) Utilize survey results from the main stakeholders in a day shelter and, 2) incorporating the voice of the houseless. The first method was a suitability study involving known aspects and locations important to the houseless community that utilized spatial analysis techniques including join, intersect, and erase. The second method utilized the results of a survey conducted by adults experiencing houselessness and their additional comments and suggestions on what factors they believe to be important. This study seeks multiple locations to meet the needs of this complex community. The first method highlights Park Place and Ward’s Corner neighborhoods, while the second method determined that downtown Norfolk, Oceanview and Military Circle would be the most optimal. Most importantly, this study highlights how factors thought to be important from a GIS analyst’s perspective are different from the most important stakeholders': the houseless community.
Printing is not supported at the primary Gallery Thumbnail page. Please first navigate to a specific Image before printing.

